Abelisaurus
Unknown
Meet Abelisaurus, a fierce dinosaur from South America. With unknown skin color and maximum speed, this carnivore remains a mystery. Belonging to the category of Dinosaurs A, it's one of the top predators of its time. Who knows what other secrets this ancient creature holds? #Abelisaurus #SouthAmerica #Carnivore
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Abelisaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
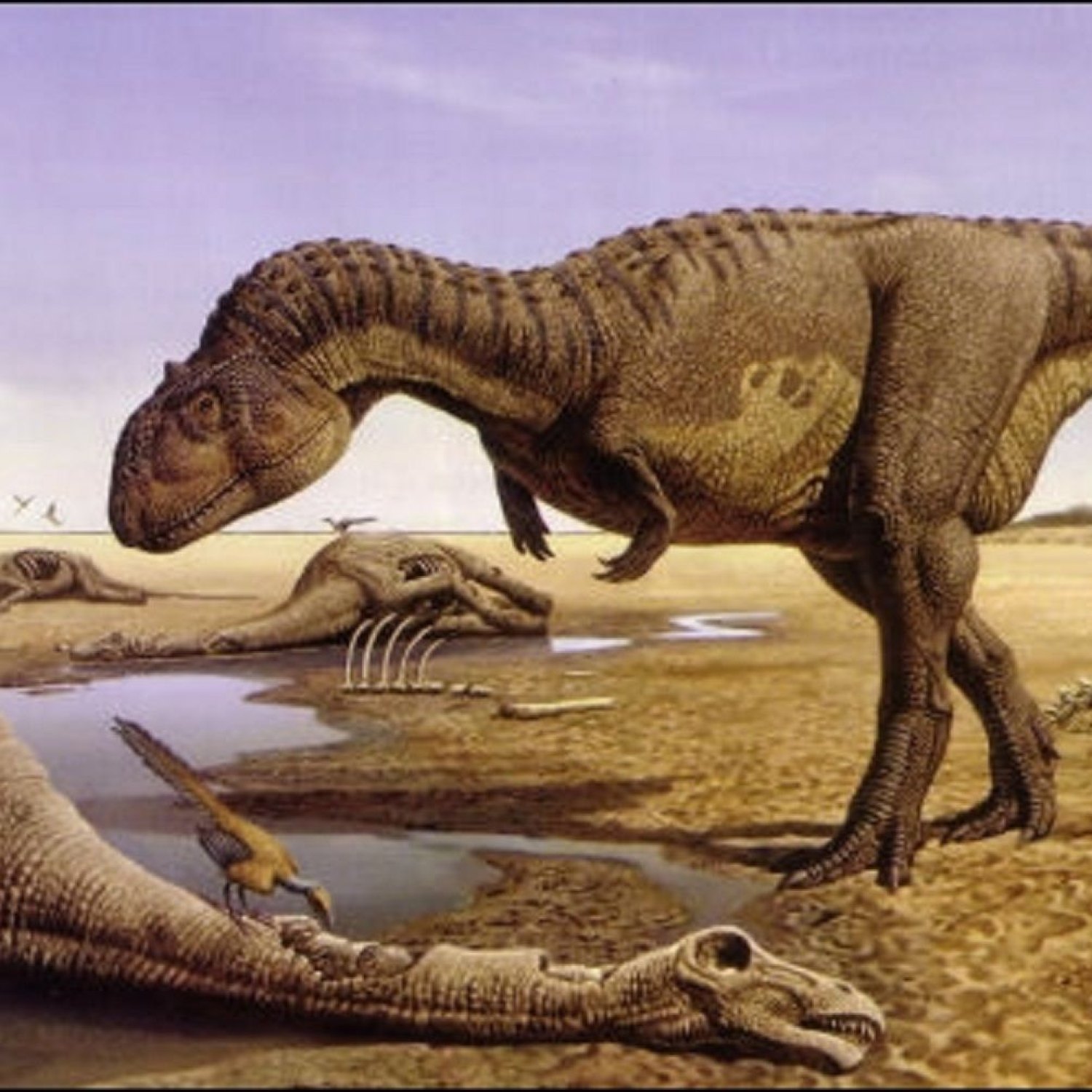
The Fearsome Abelisaurus: A Carnivorous Hunter of the Late Cretaceous Period
In the vast and diverse world of dinosaurs, some have captured our imagination more than others. From the towering Tyrannosaurus Rex to the swift Velociraptor, we have long been fascinated by these prehistoric creatures. However, there are many lesser-known dinosaurs with fascinating stories to tell. One such creature is the Abelisaurus Abelisaurus.Abelisaurus, also known as the "Abel's lizard," was a carnivorous dinosaur that roamed the Earth during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 70-80 million years ago. This fearsome predator was named after Roberto Abel, a Spanish paleontologist who discovered its remains in Argentina in the 1980s.
The Physical Characteristics of Abelisaurus
Abelisaurus was a medium-sized theropod dinosaur, with a length of 9-11 meters, a height of 2.5-3 meters, and a weight of 2-3 tons. Its body was slim and agile, making it a swift hunter. It had a small head compared to its body, with powerful jaws and numerous sharp, serrated teeth that were designed for tearing through flesh. Its strong neck and powerful hind legs also aided in its predatory behavior.One of the most distinctive physical features of Abelisaurus was its short and stunted arms. While most carnivorous dinosaurs had longer arms with functional claws, Abelisaurus had small, useless arms that were likely used for balance rather than hunting Afrovenator. This unique characteristic has puzzled paleontologists for years, with various theories trying to explain its purpose.
The Diet and Feeding Behavior of Abelisaurus
Being a theropod, Abelisaurus was a carnivorous dinosaur, meaning it mainly fed on meat. Its sharp and serrated teeth were perfect for ripping and tearing through the flesh of its prey, making it a formidable predator. Its diet primarily consisted of small to medium-sized animals, such as other dinosaurs, smaller reptiles, and even small mammals.Abelisaurus was an active predator, constantly on the hunt for its next meal. Its slender and muscular build, along with its powerful jaws, enabled it to move swiftly and catch its prey with ease. It is believed that it would have used its speed and agility to outrun and ambush its prey, much like modern-day cheetahs.
Predatory Behavior of Abelisaurus
While most dinosaurs were solitary creatures, Abelisaurus was believed to be a pack hunter. This means it would have hunted in groups, much like modern-day wolves. This predatory behavior was particularly effective in taking down larger prey, as the dinosaurs would work together to bring it down.Evidence of this pack hunting behavior was discovered when paleontologists found several fossils of Abelisaurus together in one place. This indicates that they lived and hunted in groups, proving that they were highly social creatures. This discovery has shed new light on the behavior and social lives of dinosaurs.
The Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution of Abelisaurus
Abelisaurus was a land-dwelling dinosaur, with its native habitat being the warm and lush forests of South America. During the Late Cretaceous period, South America was a landmass separate from other continents, giving rise to unique species of dinosaurs, including Abelisaurus.The fossils of Abelisaurus have only been discovered in Argentina, specifically in the Patagonia region. This was likely due to the ideal climate and abundant prey in this area, making it the perfect habitat for these fierce predators.
The Preferred Temperature and Speed of Abelisaurus
Being a native of South America, it is safe to assume that Abelisaurus preferred a warm climate. During the Late Cretaceous period, the average temperature on Earth was significantly higher than it is today, making it an ideal environment for these dinosaurs to thrive.While the maximum speed of Abelisaurus is still unknown, paleontologists can estimate its speed based on its physical characteristics and behavior. Its light and agile build, along with its pack hunting behavior, indicates that it was a fast-moving and swift predator, making it a formidable hunter on the plains of South America.
The Mysterious Skin Color of Abelisaurus
One question that has puzzled many paleontologists is the skin color of Abelisaurus. At the moment, there is no concrete evidence or fossil remains to determine the color of its skin. However, scientists have tried to guess its skin color based on the environment it lived in and its closest relatives.Being a native of South America, it is possible that Abelisaurus had a similar skin color to other dinosaurs found in this region, such as the Carnotaurus, which had a reddish-brown color. Its closest relative, the Ceratosaurus, also had a similar color, leading some to believe that Abelisaurus may have had a similar hue as well.
The Impact and Legacy of Abelisaurus
While Abelisaurus may not be as well-known as other dinosaurs, its discovery has significantly contributed to our understanding of the prehistoric world. Its unique physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat have opened up new avenues for research and furthered our knowledge of the Late Cretaceous period.The fossil remains of Abelisaurus have also provided valuable information about the social behavior of these ancient creatures. The discovery of multiple fossils together has shed new light on how these dinosaurs lived and hunted in groups, adding a new dimension to our understanding of their lives.
In popular culture, Abelisaurus has been featured in documentaries, books, and even video games. Its fierce and intimidating appearance has made it a popular subject in the media, inspiring many artists and filmmakers to include it in their work. Its legacy will continue to live on and fascinate us for generations to come.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, Abelisaurus was a fearsome and agile predator that ruled the forests of South America during the Late Cretaceous period. Its unique physical characteristics, including its short arms and sharp teeth, made it a formidable hunter. Its pack hunting behavior set it apart from other dinosaurs and shed new light on their social lives.While there is still much to discover about Abelisaurus, its legacy and impact on our understanding of the prehistoric world cannot be denied. Its discovery has helped us paint a more detailed picture of the Late Cretaceous period and continue to fuel our fascination with these ancient creatures.
Abelisaurus
Dinosaur Details Abelisaurus - Scientific Name: Abelisaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Abelisaurus
- Common Name: Abelisaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 9-11 meters
- Height: 2.5-3 meters
- Weight: 2-3 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunting in packs
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated
- Native Habitat: Land
- Geographical Distribution: South America
- Preferred Temperature: Warm
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
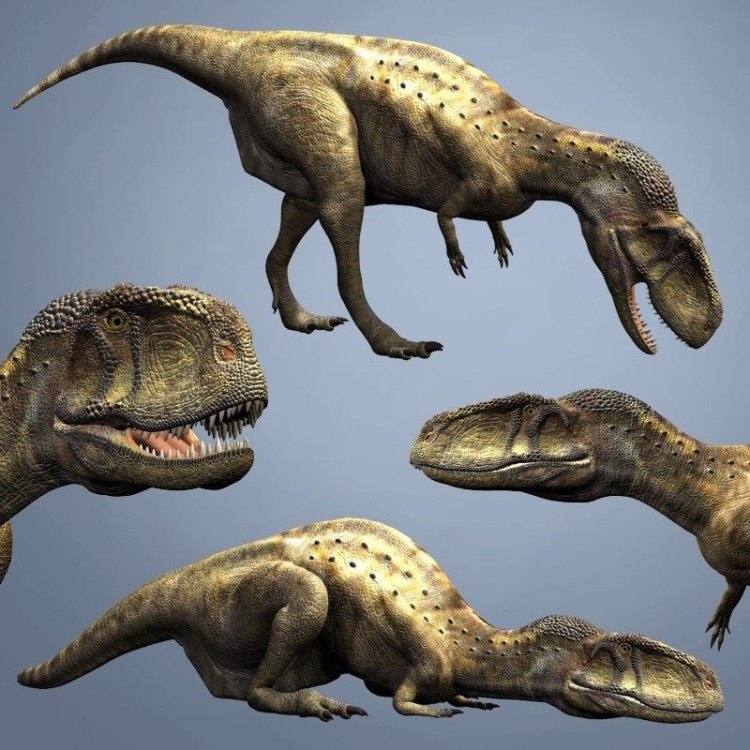

Abelisaurus
- Bone Structure: Large and sturdy
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Short arms and long hind legs
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Sharp teeth and strong jaws for hunting
- Largest Species: Abelisaurus comahuensis
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Skull and jaw fragments
- Role in Ecosystem: Apex predator
- Unique Facts: Close relative of the more famous Tyrannosaurus rex
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: Argentina
- Discovery Year: 1985
- Discoverer's Name: Dr. José Bonaparte
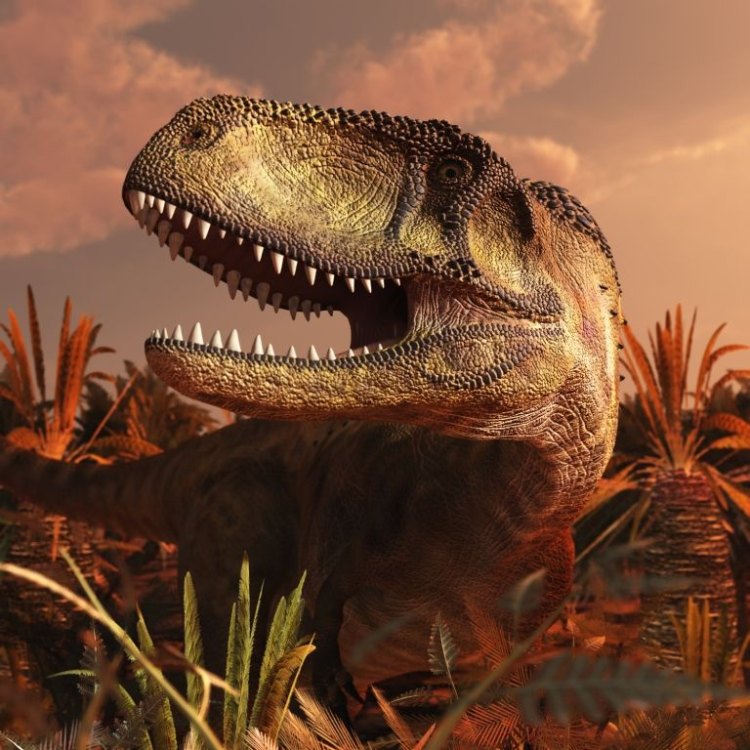

Abelisaurus
The Mighty Abelisaurus: A Ferocious Apex Predator from Argentina
Abelisaurus, a fearsome dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period, roamed the lands of present-day Argentina millions of years ago. This apex predator is one of the lesser-known dinosaurs, often overshadowed by its more famous relative, the Tyrannosaurus rex. However, Abelisaurus is a remarkable species with unique characteristics and a significant role in the ecosystem of its time.Bone Structure:
Abelisaurus had a large and sturdy bone structure, making it a formidable predator in its environment OnTimeAiraz.Com. Its body was well-adapted to walk on two legs, with a muscular tail for balance and support. Its hind legs were longer than its arms, giving it a distinct appearance and making it a swift runner. On the other hand, its short arms were not much of use in hunting or defense, but they served as a balance for the powerful bite of this ferocious creature.
Reproduction:
Like most dinosaurs, Abelisaurus reproduced by laying eggs. They were known to build nests and lay their eggs in them, similar to modern-day birds. These eggs were relatively large, about the size of a football, and they were buried in the ground for protection. These eggs eventually hatched into small but robust offspring, who would then grow into fearsome predators like their parents.
Activity Period:
Studies suggest that Abelisaurus was a diurnal or daytime hunter. This means that they were most active during the day and rested at night Acrotholus. Their sharp predatory senses would have been highly beneficial in hunting in broad daylight, allowing them to efficiently locate their preys and attack with precision.
Distinctive Features:
One of the most distinctive features of Abelisaurus was its short arms and long hind legs, giving it a unique appearance. These arms, although not useful in hunting, were well-equipped with sharp claws that could be used for protection or digging. Its hind legs, on the other hand, were powerful and muscular, enabling it to run at high speeds and chase its preys with agility.
Communication Method:
The communication method of Abelisaurus remains unknown to date. Being extinct, there is no way to study their behavior or vocalizations. However, since they were diurnal hunters, it is possible that they used visual signals or body postures to communicate with their kind.
Survival Adaptation:
Abelisaurus was a fierce predator, and its extraordinary survival adaptation reflected that. They had sharp teeth and strong jaws, ideal for sinking into the flesh of their preys. These sharp teeth were continuously replaced due to the constant wear and tear from hunting and scavenging. They also had a strong pair of jaws, enabling them to crush bones and consume even the toughest prey.
Largest Species:
The largest species of Abelisaurus was the Abelisaurus comahuensis, which could grow up to 30 feet in length and weigh more than three tons. This species is known from fragmented skulls and jawbone fossils found in Argentina, suggesting its massive size and ferocity.
Smallest Species:
Unfortunately, the smallest species of Abelisaurus is still unknown, as only two species have been discovered to date. With incomplete fossils, it is challenging to determine the size of the smaller species.
Fossil Characteristics:
The most common fossils of Abelisaurus are skull and jaw fragments. These fossils have provided essential insight into the anatomy and behavior of this mighty predator. However, complete skeletons of Abelisaurus are yet to be discovered, leaving many mysteries and unanswered questions about this species.
Role in Ecosystem:
Abelisaurus played a significant role in the ecosystem of its time as an apex predator. As one of the top predators, it helped maintain balanced and healthy populations of other species in its habitat. Its ferocity and sharp senses made it a formidable hunter, and its presence would have kept the herbivorous dinosaurs in check.
Unique Facts:
One notable unique fact about Abelisaurus is that it is a close relative of the more famous Tyrannosaurus rex, although they lived in different parts of the world. The similarities in their skeletal structures and characteristics are undeniable, making them an interesting subject of study. However, these two species diverged several million years ago, and it is uncertain if they ever encountered each other in their lifetime.
Predator Status:
Sadly, like most dinosaurs, Abelisaurus met its end when the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event occurred about 66 million years ago. This event wiped out almost all the dinosaurs, and Abelisaurus became extinct, along with its fellow predators.
Discovery Location:
The first fossils of Abelisaurus were discovered in the Argentine province of Río Negro in 1985 by renowned paleontologist Dr. José Bonaparte. These fossils were part of a larger discovery of dinosaur species in the area, making Argentina a treasure trove for paleontologists.
Discovery Year:
Abelisaurus was discovered in 1985, making it a relatively new species in the world of paleontology. Since then, it has been a subject of research and study, providing essential knowledge about the creatures that once roamed the earth.
Discoverer's Name:
Dr. José Bonaparte, a prominent Argentine paleontologist, discovered Abelisaurus. He is also credited with discovering other famous dinosaurs such as Carnotaurus and Notohypsilophodon, making him a pivotal figure in the field of paleontology.
In conclusion, Abelisaurus is a remarkable and powerful dinosaur, often overlooked by its more popular relatives. With its strong bone structure, distinctive features, and adaptation for hunting, it was a ferocious predator and a vital part of the ecosystem in its time. Thanks to the dedicated efforts of paleontologists like Dr. José Bonaparte, we can learn more about this mighty creature and gain a better understanding of the world of dinosaurs.
The Fearsome Abelisaurus: A Carnivorous Hunter of the Late Cretaceous Period
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.