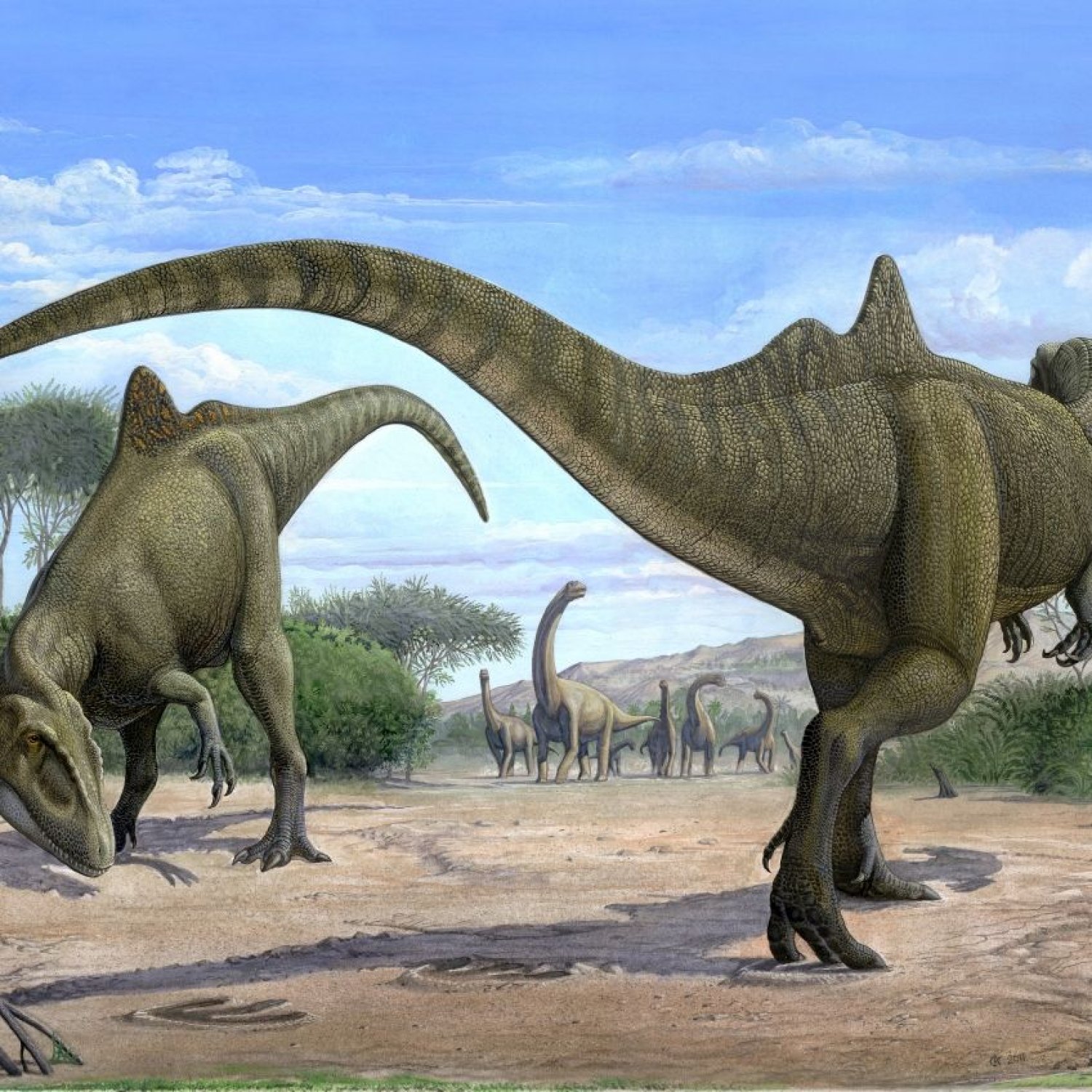
Concavenator
Unknown
Welcome to the world of dinosaurs! Meet the fearsome and lesser-known Concavenator, native to Spain. With its unknown skin color and speed, this carnivorous creature is a mystery waiting to be uncovered. Learn more about this fascinating dinosaur and its place in the prehistoric world. #Concavenator #Dinosaurs #Spain #Carnivore #Prehistoric
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Concavenator
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
Unveiling the Fascinating World of Concavenator: The Enigmatic Dinosaur from Early Cretaceous
The world of dinosaurs has always been filled with fascinating creatures that captivate our imagination. With their enormous sizes, sharp teeth, and ferocious nature, these prehistoric creatures have always been a source of wonder for us. Among the many dinosaurs that once roamed the earth, the Concavenator stands out as one of the most intriguing and mysterious species. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of Concavenator and uncover its unique characteristics that make it a standout species in the dinosaur kingdom Concavenator.Concavenator, scientifically known as Concavenator corcovatus, is a carnivorous dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous period, about 130-130 million years ago. Its name is derived from the Latin word "concavus," which means hollow, and "nator," meaning hunter. The name is a reference to the unique hump-like structure on its back, which distinguishes Concavenator from other known dinosaur species.
This enigmatic dinosaur was first discovered in 1996 in the village of Las Hoyas, in central Spain. Its skeleton was found almost entirely intact, making it one of the most well-preserved dinosaur fossils ever discovered. Since then, Concavenator has become a subject of fascination for scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike.
Standing at an impressive height of 2 meters and measuring 6-7 meters in length, Concavenator was relatively smaller in size compared to other large theropods like Tyrannosaurus Rex. However, what makes this dinosaur truly remarkable is its unique physical characteristics and behaviors.
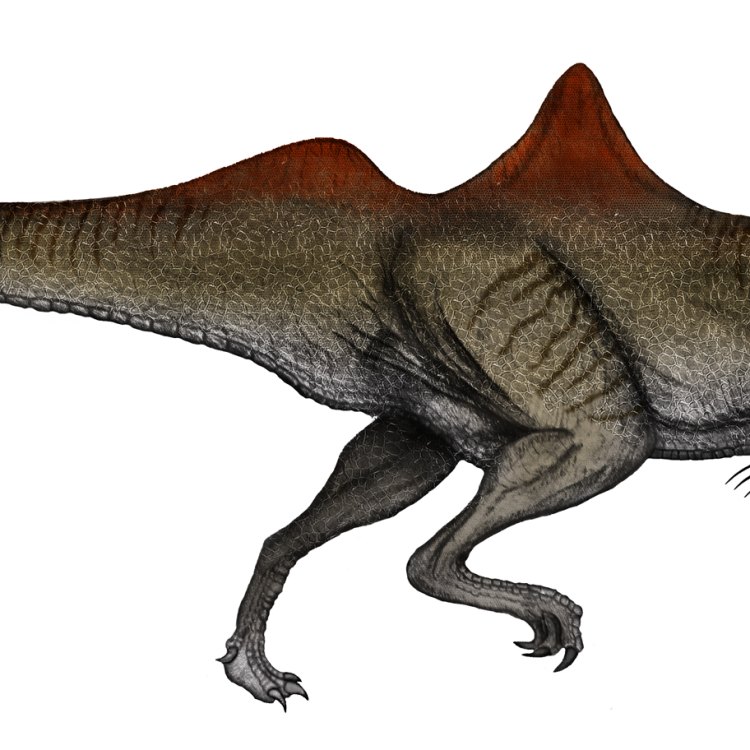
Concavenator's most distinguished feature is the raised hump on its back, which is believed to have been supported by strong spine bones Chindesaurus. This unique hump also gave Concavenator its nickname "The Humpback Hunter." Scientists speculate that the hump may have served several purposes, including fat storage, display to attract mates, or even as a means of communication.
Another striking physical feature of Concavenator is its long arms that ended in three fingers with sharp claws. This is a unique characteristic among theropod dinosaurs, as most of them had only two fingers. The long arms and sharp claws of Concavenator indicate that it was an active predator, capable of swift movements and deadly attacks.
Like most theropods, Concavenator was also a carnivore, and its diet consisted mainly of other dinosaurs. However, one of its most distinctive predatory behaviors was its ambush hunting technique. Concavenator's long arms and sharp teeth gave it an advantage in surprise attacks, making it a formidable predator.
Speaking of teeth, Concavenator had a set of blade-like teeth that was perfectly suited for slicing through flesh and tearing apart its prey. While most theropods had sharper, pointed teeth, Concavenator's teeth were unique in their shape, making it a specialist in consuming large animals.
The native habitat of Concavenator was terrestrial, and it is believed to have lived in a tropical climate. Its fossils were unearthed in Spain, and a closer examination of its remains suggests that it was well adapted to the hot and dry conditions of the region.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Concavenator is its geographical distribution. Fossils of this dinosaur have only been discovered in Spain, making it an exclusively Spanish species. This has led scientists to believe that Concavenator may have evolved and adapted to the specific conditions of the Iberian Peninsula.
The maximum speed of Concavenator is still unknown, as scientists are yet to find any evidence of its locomotion abilities. However, based on its physical features and predatory behavior, it is believed that this dinosaur was a swift runner, capable of outrunning its potential prey.
Another aspect of Concavenator that remains a mystery is its skin color. With no fossil evidence of pigmentation, it is impossible to determine the color of its skin. This opens up room for speculation, with some theories suggesting that it may have had a camouflage pattern, while others believe it may have had bright, eye-catching colors to attract mates.
Despite the many mysteries surrounding Concavenator, scientists have been able to uncover some of its standout features, thanks to the well-preserved fossils. Its unique hump and long arms have led to a lot of speculation about its behavior and lifestyle, making it a subject of ongoing research.
In the world of dinosaurs, Concavenator is a true enigma, with its distinct physical features, feeding and predatory behaviors, and mysterious characteristics. Its discovery has shed light on the diverse and complex world of dinosaurs and has fueled our curiosity to learn more about these incredible creatures that once ruled the earth.
In conclusion, Concavenator is a standout species in the dinosaur kingdom, with its unique physical characteristics and behaviors. Its discovery in Spain has not only expanded our knowledge of prehistoric life but also sparked new avenues for research and understanding about the diversity of dinosaurs. We can only hope that as scientists continue to uncover more fossils, we may finally unravel all the mysteries surrounding this fascinating and mysterious dinosaur.

Concavenator
Dinosaur Details Concavenator - Scientific Name: Concavenator corcovatus
- Category: Dinosaurs C
- Scientific Name: Concavenator corcovatus
- Common Name: Concavenator
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: 6-7 meters
- Height: 2 meters
- Weight: 1-2 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Ambush hunting
- Tooth Structure: Blade-like teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: Spain
- Preferred Temperature: Tropical climate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
Concavenator
- Bone Structure: Lightweight and hollow bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Raised hump on its back
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Camouflage
- Largest Species: Concavenator corcovatus
- Smallest Species: Concavenator corcovatus
- Fossil Characteristics: Nearly complete skeleton with preserved skin impressions
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: Had a distinctive hump on its back
- Predator Status: Apex predator
- Discovery Location: Las Hoyas, Spain
- Discovery Year: 2010
- Discoverer's Name: Ortega, Escaso, and Sanz
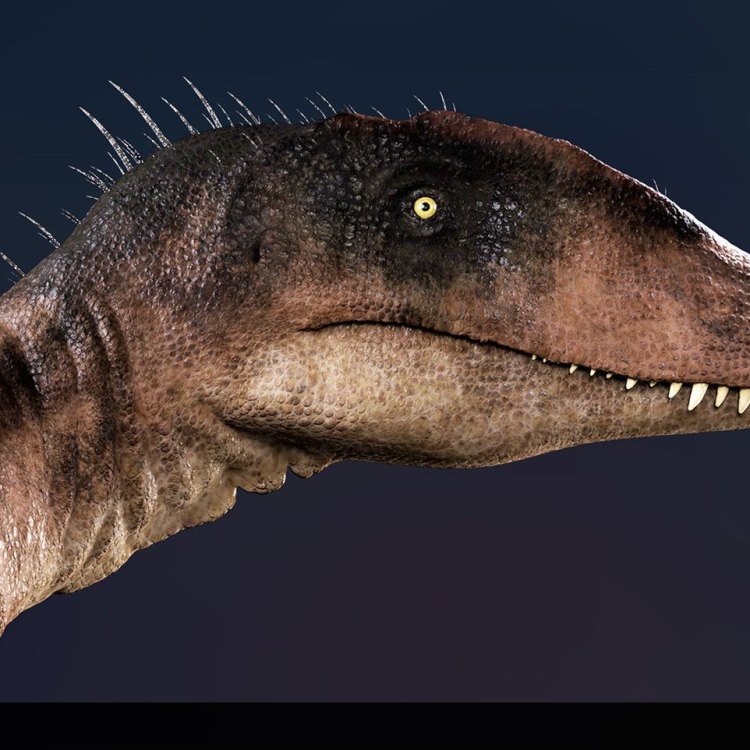

Concavenator corcovatus
The Fascinating Story of Concavenator: The Top Predator of Ancient Spain
Deep in the heart of Spain, in a small village named Las Hoyas, a team of paleontologists uncovered a remarkable discovery in 2010. It was the nearly complete skeleton of a dinosaur that roamed the Earth over 100 million years ago. This dinosaur was unlike any other that had been found before, and it would soon capture the attention of the world.This incredible creature was given the name Concavenator corcovatus, derived from the Latin word “concavus” meaning “hollow” and “corcovare” meaning “hump OnTimeAiraz.Com.” This unique name perfectly describes the defining feature of this dinosaur, a raised hump on its back that set it apart from all other known dinosaur species. But the hump was just the beginning of the many amazing characteristics of Concavenator, making it one of the most intriguing and enigmatic dinosaurs in history.
From its lightweight and hollow bones to its egg-laying reproduction method and diurnal activity period, Concavenator had several distinctive features that made it stand out from other known species. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating story of Concavenator, the top predator of ancient Spain.
Bone Structure: Lightweight and Hollow Bones
One of the most distinctive and unique features of Concavenator is its lightweight and hollow bones. These bones were a remarkable adaptation that allowed this dinosaur to be both quick and agile, making it a formidable hunter.The lightweight bones of Concavenator were not only helpful in its movement, but they also played a crucial role in its survival. As a large predator, Concavenator needed to have a strong and durable skeletal structure, but at the same time, it had to be fast and agile to catch its prey. The hollow bones not only made it possible for Concavenator to achieve this balance, but it also reduced its overall weight, allowing it to move with more ease and efficiency Cryptovolans Pauli.
These hollow bones were also a strong indicator of its avian-like ancestry. Similar adaptations can be seen in modern-day birds, which evolved from dinosaurs like Concavenator. This evolutionary trait is a testament to the diversity and adaptability of these ancient creatures.
Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
Like most dinosaurs, Concavenator had a unique reproductive method that sets it apart from modern-day mammals. This species was an egg-laying dinosaur, also known as an oviparous species. This meant that it laid eggs to bring forth its offspring rather than giving birth to live young like most mammals do.The eggs of Concavenator were likely laid in nests and incubated until they hatched, which may have taken several months. This reproductive method allowed for a larger number of offspring to be produced at once, increasing the chances of survival for this species. It also allowed for more independence in the young, which could start fending for themselves soon after hatching.
Interestingly, the egg-laying method is still prevalent in many non-avian dinosaurs and modern-day birds. It is an evolutionary trait that proves the successful reproduction and survival of these species over millions of years.
Activity Period: Diurnal
Another unique characteristic of Concavenator is its diurnal activity period, meaning it was active during the day and rested at night. This sets it apart from many other known theropod dinosaurs that were believed to be nocturnal or crepuscular (active at dawn and dusk).Scientists have determined this activity period by studying the bone structure and growth rings of Concavenator’s bones. The growth rings, similar to the rings on a tree trunk, can reveal information about the dinosaur's growth and development. By analyzing these rings, scientists have concluded that Concavenator was active during the day, hunting and foraging for food.
The diurnal activity period was a vital adaptation that allowed Concavenator to thrive in its environment. Its prey, which consisted of smaller dinosaurs and other animals, were also active during the day, making it easier for Concavenator to hunt and catch its prey.
Distinctive Features: Raised Hump on its Back
Of all the unique features of Concavenator, its most striking one is the raised hump on its back. This hump is what gave the dinosaur its name, “Concavenator corcovatus,” which translates to “humpback hunter.”This hump was a distinctive feature that set Concavenator apart from all other known dinosaur species. It was formed by long neural spines, up to 17 inches in length, protruding from the vertebrae of its back. These spines supported a large and muscular hump, likely used for storing fat and muscles for energy during times of low food availability.
Scientists are still unsure of the exact purpose of the hump, but it is believed that it could have also served as a display feature to attract potential mates or establish dominance in its social hierarchy. Whatever its function may have been, the hump made Concavenator a truly unique and remarkable creature.
Communication Method: Unknown
Communication is a crucial aspect of any animal's behavior, helping them to interact and establish social relationships with others. However, due to the lack of evidence, we know very little about how Concavenator communicated with other dinosaurs.As a solitary predator, it is unlikely that Concavenator relied heavily on vocalizations to communicate. Instead, it may have used body language and scents to communicate with its own kind and other species. However, until more evidence is found, the exact communication method of Concavenator remains a mystery.
Survival Adaptation: Camouflage
In the world of dinosaurs where predators and prey were constantly on the lookout for each other, survival was all about being able to blend in with the environment. Concavenator had a remarkable survival adaptation that helped it to evade predators and sneak up on its prey - camouflage.The skin impressions found on the fossil of Concavenator showed a unique pattern of scales and coloration that allowed it to blend in with its surroundings. This camouflage would have made it tough for other dinosaurs to spot Concavenator, giving it a significant advantage in its survival and hunting abilities.
The camouflage also helped Concavenator to regulate its body temperature, as it was a ectothermic (cold-blooded) dinosaur. The coloration of its skin would have helped it to absorb heat from the sun, and the scales acted as insulation, keeping its body warm.
Largest Species: Concavenator corcovatus
Concavenator corcovatus is the only species of this dinosaur that has been discovered so far. It was estimated to be around 20 feet long and weighed around 2,500 pounds, making it one of the largest known theropods of its time.Given its size and predatory behavior, Concavenator likely had no natural predators and was considered an apex predator in its ecosystem. This allowed it to roam freely and dominate its surroundings, making it a truly remarkable and powerful creature.
Smallest Species: Concavenator corcovatus
While there have been no discoveries of smaller species of Concavenator, it is worth noting that the only known species, Concavenator corcovatus, was the same size regardless of age or gender. This is quite unusual in the world of dinosaurs, as most species had a significant size difference between males and females, and individuals of different ages.The consistent size of Concavenator corcovatus could be an indication of its social structure and behavior, suggesting that they may have lived and hunted alone rather than in groups. However, further research and discoveries are needed to confirm this.
Fossil Characteristics: Nearly Complete Skeleton with Preserved Skin Impressions
The discovery of Concavenator has been nothing short of a paleontological dream come true. The nearly complete skeleton found in Las Hoyas revealed an abundance of information and evidence about this mysterious dinosaur.The fossil of Concavenator was not only a nearly complete skeleton, but it also held the preserved impressions of its skin. This was a rare and incredible discovery as it provided scientists with crucial information about its physical appearance and behavior. The skin impressions showed a unique skin pattern and scale morphology, indicating its camouflage adaptation and ectothermic nature.
This discovery was a remarkable feat that has added to our knowledge and understanding of dinosaurs, specifically theropod species.
Role in Ecosystem: Top Predator
As an apex predator, Concavenator played a crucial role in its ancient ecosystem. It sat at the top of the food chain, preying on smaller dinosaurs and other animals, keeping the population of its prey in check.The presence of a top predator like Concavenator was essential for maintaining a balance in the ecosystem, ensuring that no one species dominated and caused harm to other species. Its role as a predator was crucial for the survival and evolution of other species in its environment, making it an essential and influential part of its ecosystem.
Unique Facts: Had a Distinctive Hump on its Back
Concavenator has several unique and intriguing characteristics, but its distinctive hump on its back remains one of the most memorable and fascinating features. This feature not only allowed the dinosaur to be quick and agile, but it also served as a display feature, a storage unit, and a survival adaptation.It is this unique hump that has captured the imagination of people worldwide, making Concavenator one of the most talked-about and popular dinosaurs in history.
Predator Status: Apex Predator
As mentioned earlier, Concavenator was an apex predator,

Unveiling the Fascinating World of Concavenator: The Enigmatic Dinosaur from Early Cretaceous
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.