Dysalotosaurus
Unknown
Dysalotosaurus, or noble lizard, was a plant-eating dinosaur found in Tanzania. Despite its name, its skin color is still a mystery. While its maximum speed is unknown, its powerful legs suggest it was a fast runner. Its fossils provide valuable insights into the diverse and fascinating world of dinosaurs. #Dysalotosaurus #Dinosaurs #Paleontology
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Dysalotosaurus
Geological Era: Late Jurassic
Feeding Behavior: Browsing herbivore
Dysalotosaurus: Unlocking the Mysteries of the Late Jurassic Herbivore
In the vast and diverse prehistoric world, few creatures are as fascinating and awe-inspiring as the dinosaurs. These ancient reptiles ruled the earth for millions of years, and despite their extinction, continue to captivate our imagination. Among them, one particularly intriguing species is Dysalotosaurus, a large herbivorous dinosaur that inhabited the land during the Late Jurassic period.Named after the Greek word 'dysalotos', meaning difficult to capture, Dysalotosaurus lived approximately 155 to 148 million years ago in the African country of Tanzania Dysalotosaurus. This dinosaur is a relatively recent discovery, and although its remains were first identified in the 1940s, it was not until the 21st century that it was officially classified as its own genus. Today, Dysalotosaurus remains shrouded in mystery, but paleontologists continue to study this magnificent creature, hoping to unravel its secrets and shed light on its place in the prehistoric world.
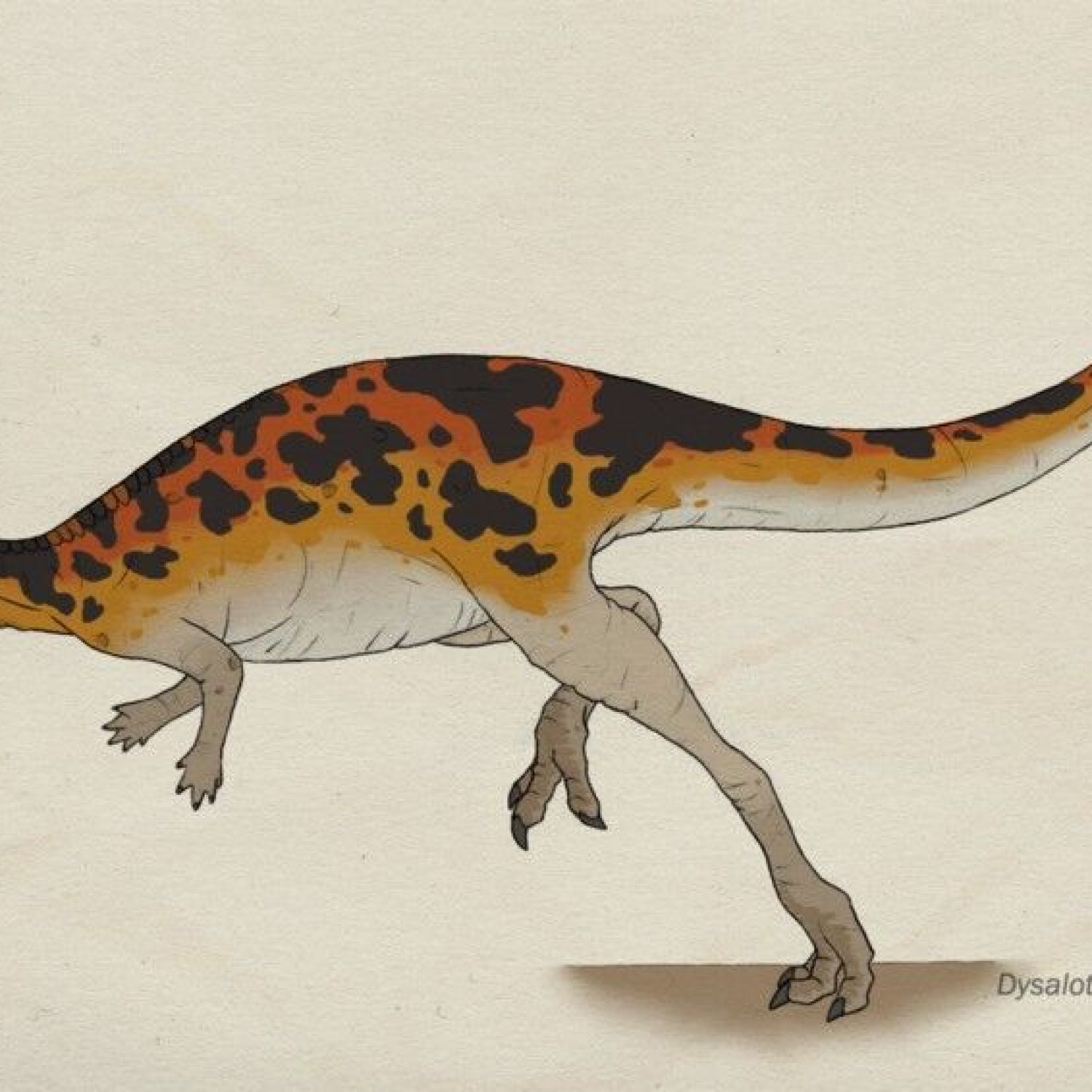
With a scientific name that matches its common name, Dysalotosaurus belongs to the same family as other well-known herbivorous dinosaurs like the Stegosaurus and the Diplodocus. It is estimated that this dinosaur measured around 7 to 8 meters in length and stood at an impressive height of 2.5 meters. Weighing between 2 to 3 tons, Dysalotosaurus was a massive animal, able to tower over most of its contemporaries.
As a herbivore, Dysalotosaurus had a diet consisting mainly of plants. This is evident from its characteristic leaf-shaped teeth, which were perfect for tearing and chewing vegetation. The tooth structure of this dinosaur is one of its standout features, and it helps us understand its feeding behavior Doryaspis. Unlike other herbivorous dinosaurs that were grazers, Dysalotosaurus was a browsing herbivore. This means that it would pluck leaves and branches from trees and shrubs, rather than feeding on low-lying vegetation.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Dysalotosaurus is its predatory behavior, or rather, its lack thereof. Unlike other large dinosaurs that were either apex predators or had some degree of predatory behavior, Dysalotosaurus was strictly a non-predatory animal. Its peaceful nature is reflected in its physical characteristics, such as the lack of sharp claws, which would have been useful for hunting and killing prey.
Dysalotosaurus was well-adapted to its life on land, and its anatomy reflects that. Its strong and sturdy legs, combined with its large body, allowed it to navigate various terrains with ease. This made it a versatile and robust creature, well-equipped to survive in its native habitat. Its native habitat was the African continent, specifically present-day Tanzania, during the Late Jurassic period. This area was characterized by warm and temperate temperatures, making it the perfect environment for the herbivorous Dysalotosaurus.
Today, the fossils of Dysalotosaurus are only found in Tanzania, but back in the Late Jurassic era, its geographical distribution may have been much wider. It is believed that this dinosaur could have roamed other parts of Africa, as well as other continents, but the lack of evidence makes it difficult to confirm. Paleontologists continue to search for more fossils, hoping to expand our understanding of the range of Dysalotosaurus during its time on earth.
One of the most commonly asked questions about Dysalotosaurus is its maximum speed. Unfortunately, there is no conclusive answer to this question, as there is no evidence indicating the maximum speed of this dinosaur. However, based on its anatomy and size, it is believed that Dysalotosaurus was not particularly fast, as its large body and short legs would have hindered its mobility.
Another aspect of Dysalotosaurus that remains a mystery is its skin color. Unlike many other dinosaurs, Dysalotosaurus has not been depicted in popular media, making it difficult to speculate on its appearance. Since there is no evidence of fossilized skin, paleontologists can only make educated guesses about the color of this dinosaur's skin. However, one theory suggests that it may have had a green or brown color to camouflage itself in its natural habitat.
In conclusion, Dysalotosaurus is a fascinating and enigmatic creature that continues to captivate our imagination. With its massive size, unique feeding behavior, and lack of predatory behavior, it stands out among the many herbivorous dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic period. While there is still much to learn about this magnificent creature, its discovery and classification have already added to our understanding of the prehistoric world.
As paleontologists continue to unearth new fossils and study existing ones, we can look forward to finding more answers about Dysalotosaurus and its place in the Late Jurassic ecosystem. Until then, we can only marvel at this mysterious dinosaur and imagine what life was like for a creature that walked the earth millions of years ago.
Dysalotosaurus
Dinosaur Details Dysalotosaurus - Scientific Name: Dysalotosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs D
- Scientific Name: Dysalotosaurus
- Common Name: Dysalotosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Jurassic
- Length: 7-8 meters
- Height: 2.5 meters
- Weight: 2-3 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing herbivore
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Land
- Geographical Distribution: Africa (Tanzania)
- Preferred Temperature: Warm and temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
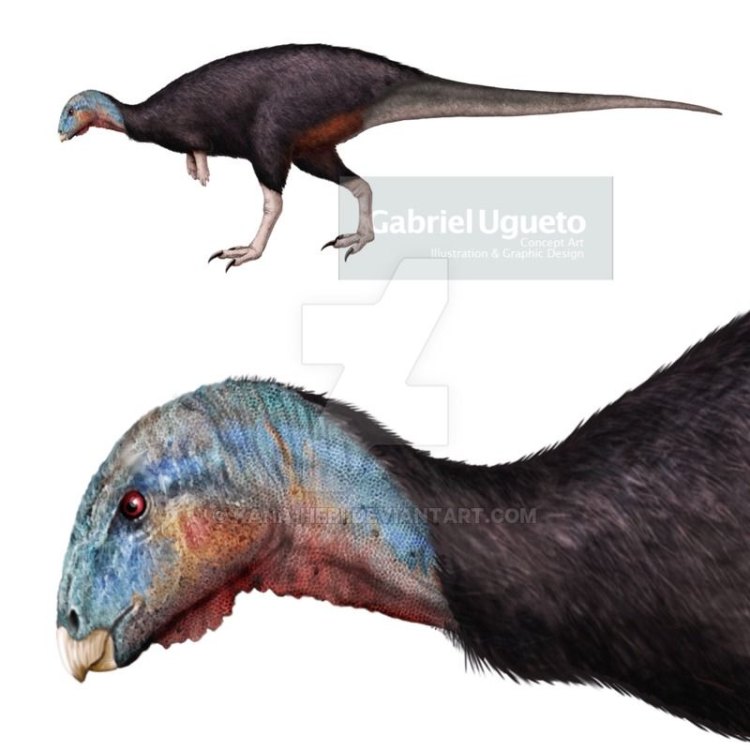

Dysalotosaurus
- Bone Structure: Skeletal structure similar to other large sauropods
- Reproduction Type: Sexual reproduction
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Narrow skull with elongated snout
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Large size for defense against predators
- Largest Species: Dysalotosaurus lettowvorbecki
- Smallest Species: Dysalotosaurus pruneri
- Fossil Characteristics: Fossilized remains of bones and teeth
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous grazer
- Unique Facts: The only known dinosaur species from Tanzania
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Tendaguru Formation, Tanzania
- Discovery Year: 1911
- Discoverer's Name: Werner Janensch

Dysalotosaurus
The Unique Features of Dysalotosaurus: Tanzania's Hidden Dinosaur
In the land of the Serengeti and Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania may be best known for its breathtaking landscapes and diverse wildlife, but hidden within its rich history lies a unique dinosaur species - Dysalotosaurus.Discovered over a century ago, Dysalotosaurus has remained a mystery to scientists due to its limited fossil record. However, with recent advancements in technology and paleontological research, we are beginning to uncover the fascinating and distinctive features of this ancient creature.
So, what makes Dysalotosaurus stand out from its dinosaur counterparts? Let's dive in and explore the unique characteristics and role of this elusive species in the African ecosystem OnTimeAiraz.Com.
The Bone Structure of Dysalotosaurus
Dysalotosaurus belonged to the family of sauropod dinosaurs, known for their large size and long necks. Similar to its sauropod relatives, Dysalotosaurus had a massive skeletal structure, with four thick legs and a long tail for balance.What sets this herbivorous dinosaur apart is its narrow skull with an elongated snout, resembling that of a horse. This unique feature may have helped Dysalotosaurus in reaching vegetation from higher branches, giving it an advantage in a competitive grazing environment.
Reproduction and Activity
Evidence suggests that Dysalotosaurus reproduced through sexual means, which is common in most dinosaurs. It is believed that they laid eggs, which were then incubated until hatching. As large animals, Dysalotosaurus likely lived in small herds to increase their chances of survival and protect their young.Another distinctive characteristic of this dinosaur was its activity period. Dysalotosaurus was diurnal, meaning it was active during the day and rested at night Demandasaurus. This is in contrast to some other sauropods, who were primarily active at night.
Communication and Survival Adaptation
One aspect of Dysalotosaurus that remains a mystery is its method of communication. As dinosaurs were not known for their advanced vocalizations, it is likely that Dysalotosaurus communicated through physical cues, such as body postures and displays.As grazers in a time when predators roamed freely, Dysalotosaurus had to adapt to survive. Its large size and towering height may have acted as a defensive mechanism against predators, deterring them from attacking. This adaptation allowed for Dysalotosaurus to thrive and live longer in the African ecosystem.
The Largest and Smallest Species
Out of all the known Dysalotosaurus species, the largest and most well-known is the Dysalotosaurus lettowvorbecki. This species could reach lengths of up to 15 meters, making it one of the largest sauropods in Africa during its time.On the other end of the spectrum, the smallest Dysalotosaurus species is the Dysalotosaurus pruneri, which was estimated to be around 8 meters in length. Despite its smaller size, it still had the distinctive features of its larger counterparts, including the narrow skull and elongated snout.
The Fossil Characteristics of Dysalotosaurus
The first evidence of Dysalotosaurus was found in the Tendaguru Formation in Tanzania in 1911 by German paleontologist, Werner Janensch. This location is famous for its high concentration of dinosaur fossils, including those of other sauropod species.Fossilized remains of bones and teeth have allowed scientists to reconstruct the skeletal structure and size of Dysalotosaurus. However, due to the limited fossil record, there is much that still remains unknown about this species.
The Role of Dysalotosaurus in the Ecosystem
As a herbivorous grazer, Dysalotosaurus played a crucial role in the African ecosystem. By consuming large quantities of vegetation, it helped in maintaining the balance of the food chain, providing sustenance to other animals.Additionally, their massive size and distinctive features may have also played a role in the ecosystem dynamics. The presence of such large herbivores may have shaped the landscape and influenced the evolution of other species.
The Unique Facts of Dysalotosaurus
Apart from being the only known dinosaur species from Tanzania, Dysalotosaurus holds other unique facts that make it a fascinating subject of study. As the oldest known sauropod in Africa, it provides valuable insights into the evolution and paleontology of this region.Despite being discovered over a hundred years ago, Dysalotosaurus remains a relatively unknown dinosaur species. However, with continued research and advancements in technology, we are slowly unlocking the secrets of this elusive creature.
The Non-Predatory Status of Dysalotosaurus
Contrary to popular belief, Dysalotosaurus was a non-predatory species. While its large size and sharp teeth may suggest otherwise, evidence supports the theory that this dinosaur was a gentle giant, solely relying on vegetation for sustenance.This non-predatory status has contributed to the mystery surrounding Dysalotosaurus, with little understanding of what may have led to its extinction.
In conclusion, Dysalotosaurus may be a lesser-known dinosaur, but its distinctive features and role in the African ecosystem make it a crucial part of our understanding of prehistoric life. With ongoing research and exploration, we can continue to unravel the unique characteristics of this Tanzania's hidden dinosaur.

Dysalotosaurus: Unlocking the Mysteries of the Late Jurassic Herbivore
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.