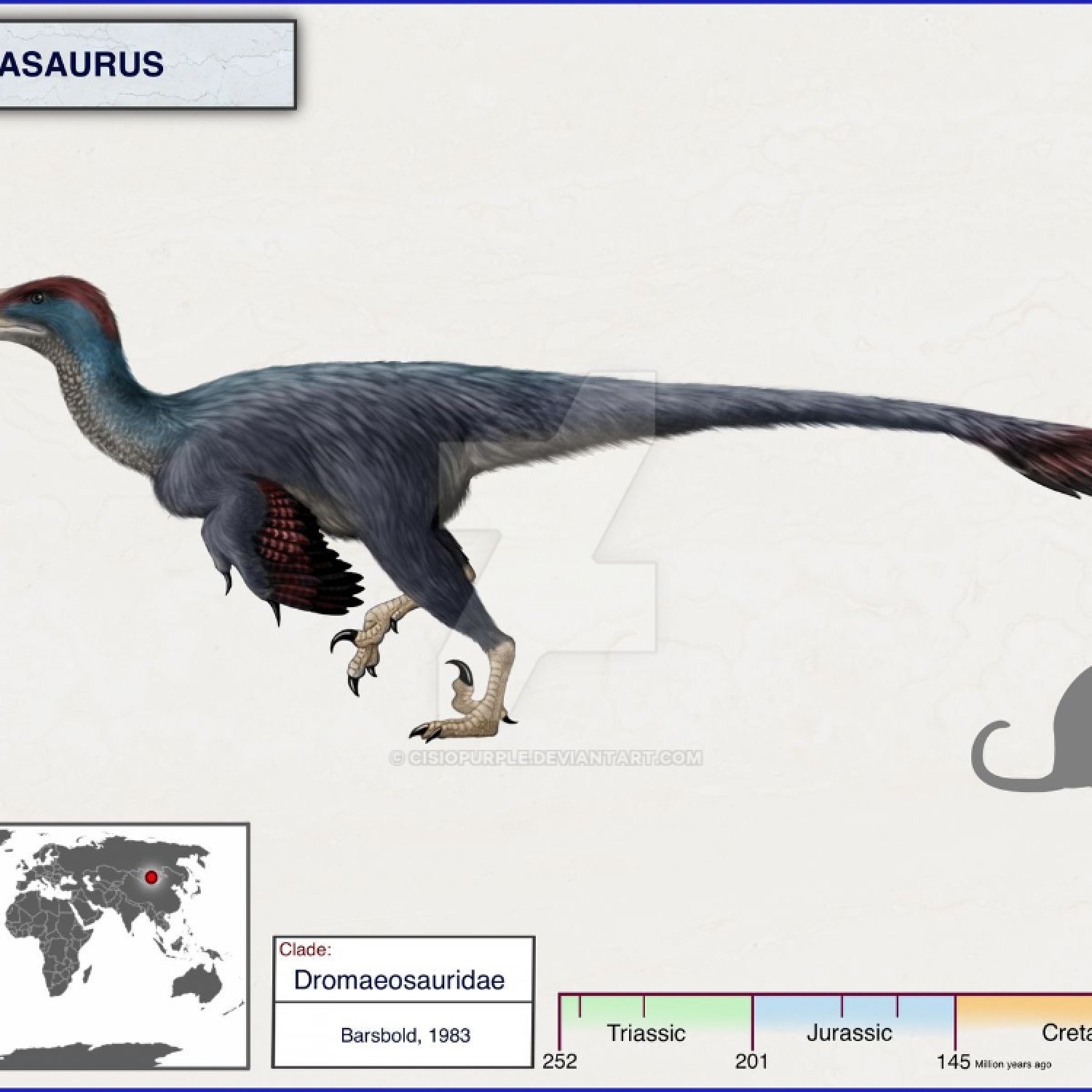
Adasaurus
Unknown
Adasaurus, a meat-eater from Mongolia, roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Its skin color remains a mystery, but its ferocious appetite and unknown speed make it a formidable predator. Discover more about this enigmatic dinosaur. #Adasaurus #Mongolia #Dinosaurs #Paleontology
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Adasaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Carnivore
The Intriguing Story of Adasaurus: A Small but Fierce Late Cretaceous Dinosaur
Gather around, dinosaur lovers, and get ready to travel back in time to the Late Cretaceous era, where our protagonist, Adasaurus, roamed the Earth. This small, yet fierce predator has a captivating story that will surely capture your curiosity. From its sharp tooth structure to its preferred habitat, let's dive into the details of this fascinating creature.Introduction to Adasaurus
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of Adasaurus, let's first understand what type of dinosaur it is Adasaurus. Adasaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur that belonged to the Late Cretaceous period, which lasted from 99 million to 65 million years ago. It is a small-sized dinosaur, measuring only 3 meters in length, 1 meter in height, and weighing around 200 kilograms. Its scientific name, "Adasaurus," comes from the word "Ada," the name of the wife of the Russian paleontologist, Evgeny Aleksandrovich Maleev, who discovered its fossils in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia in 1948.Diet and Feeding Behavior
Despite its small size, Adasaurus was a formidable predator, with a diet consisting mainly of meat, making it a carnivore. Its sharp and serrated teeth were its primary weapon for hunting and feeding. These teeth were designed to tear through flesh and hold onto its prey, allowing Adasaurus to have a firm grip while tearing its meal apart. Its jaw structure also played a crucial role in its feeding behavior, as it could open wide and deliver a powerful bite.Predatory Behavior
Based on its physical features, scientists believe that Adasaurus was a highly active predator. Its small size and agility allowed it to move swiftly through the dense, wooded environments in which it lived Avimimus Portentosus. Its sharp teeth, powerful jaw, and nimble movements made it a relentless and fierce predator, hunting down smaller prey like small mammals and reptiles.Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Adasaurus fossils have only been discovered in Mongolia, making it endemic to that region. The Gobi Desert in Mongolia is known to have been a densely wooded environment during the Late Cretaceous period, which was the preferred habitat of Adasaurus. The dense vegetation provided ample cover for this predator to hunt down its prey, making it an ideal location for its survival.The Mystery Behind Adasaurus' Skin Color and Preferred Temperature
While we know a great deal about Adasaurus's physical features, there is still a great deal of unknowns about it. One of the biggest mysteries is its skin color and preferred temperature. Unfortunately, these details have not been preserved in the fossils found, making it impossible for scientists to determine its skin color and preferred temperature.Maximum Speed and Adaptations
Another aspect that is yet to be determined about Adasaurus is its maximum speed. Its small size and agility suggest that it was a quick and nimble creature, but there is no concrete evidence to support this theory. Additionally, Adasaurus had adaptations that allowed it to survive in its densely wooded environment. Its sharp claws helped it move through the thick vegetation, and its binocular vision allowed it to have a better depth perception, making it easier for it to hunt and avoid any potential dangers.In Conclusion
Adasaurus may be a lesser-known dinosaur, but its story is no less intriguing than other popular dinosaurs. Its small size and fierce predatory behavior make it stand out in the vast world of dinosaurs. While there is still a lot we don't know about Adasaurus, the fossils that have been discovered have provided us with valuable insights into its physical features, diet, and predatory behavior. As technology and research continue to advance, who knows what else we may discover about this fascinating creature that once roamed the Earth in the Late Cretaceous era.
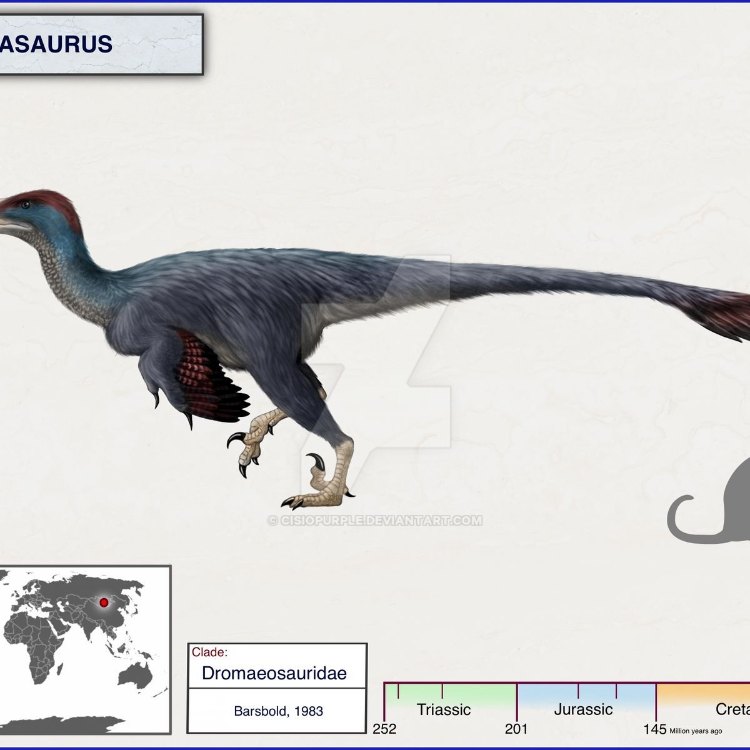
Adasaurus
Dinosaur Details Adasaurus - Scientific Name: Adasaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Adasaurus
- Common Name: Adasaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 3 meters
- Height: 1 meter
- Weight: 200 kilograms
- Diet: Meat
- Feeding Behavior: Carnivore
- Predatory Behavior: Active predator
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: Wooded environments
- Geographical Distribution: Mongolia
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
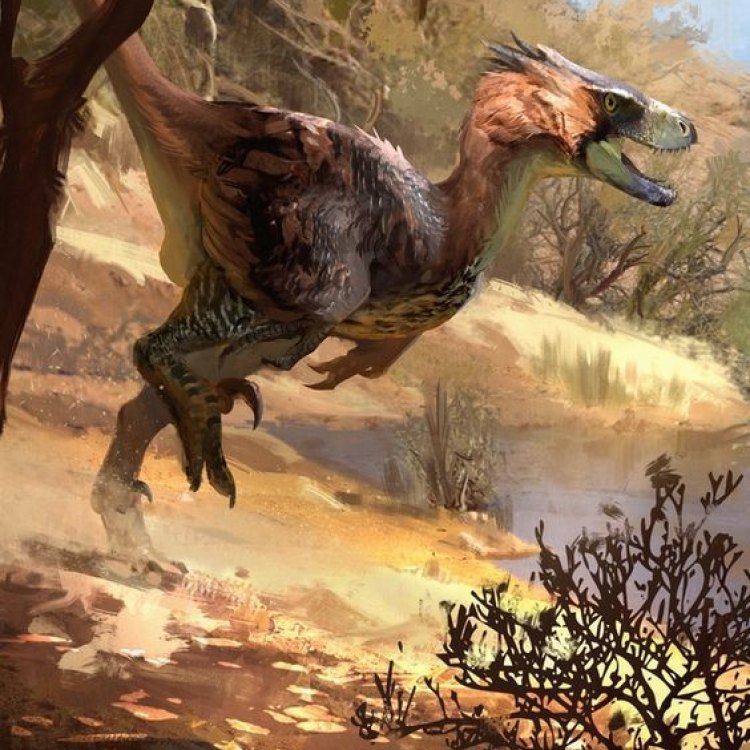

Adasaurus
- Bone Structure: Lightweight
- Reproduction Type: Egg laying
- Activity Period: Daytime
- Distinctive Features: Large sickle-shaped claw on the second toe of each foot
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Agile runner and predator
- Largest Species: Adasaurus mongoliensis
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skeleton
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator in its habitat
- Unique Facts: Possessed long, thin neck and a short snout
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: Mongolia
- Discovery Year: 1983
- Discoverer's Name: N. N. Chinzorig
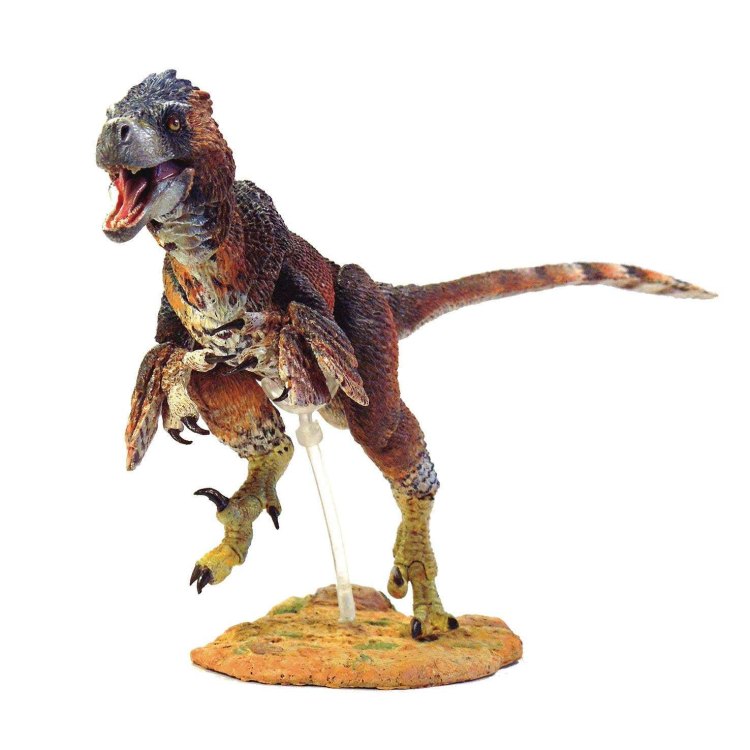

Adasaurus
Adasaurus: The Agile Runner and Top Predator of Mongolia
Deep in the wilderness of the Gobi Desert, lies the fossilized remains of a fierce creature that roamed the Earth over 70 million years ago. Known for its distinctive sickle-shaped claw and agile running abilities, the Adasaurus was a formidable predator in its habitat. Despite being a relatively unknown species, its unique features and significant role in the ecosystem make it a fascinating subject of study for paleontologists.The Adasaurus, meaning "Ada's lizard" in Greek, was first discovered in 1983 in Mongolia by a local paleontologist named N OnTimeAiraz.Com. N. Chinzorig. Its name was derived from the daughter of one of the team members who found the first specimen. Since then, more bones have been unearthed, giving scientists valuable information about this enigmatic creature.
One of the most distinctive features of the Adasaurus is its large sickle-shaped claw on the second toe of each foot. This claw, measuring about 8 inches long, was used as a lethal weapon, primarily for hunting and defending itself against predators. The sickle claw was sharp and could inflict severe injuries, making the Adasaurus a force to be reckoned with.
Apart from its deadly claw, the Adasaurus also possessed a long, thin neck and a short snout, giving it a unique appearance among other theropod dinosaurs. This feature also suggests that it may have had a more specialized feeding mechanism, possibly targeting smaller and more elusive prey Amygdalodon.
Adasaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur belonging to the family Dromaeosauridae, which includes the famous Velociraptor and Deinonychus. It is one of the smallest known dromaeosaurids, with the largest species, Adasaurus mongoliensis, estimated to be around 6 feet in length and weighing about 50 pounds. The smallest species, however, is still unknown.
Despite its small size, the Adasaurus had adapted to become a skilled runner, giving it a significant advantage in its pursuit of prey. Its lightweight bone structure, characterized by thin and hollow bones, allowed it to move swiftly and with agility. Its long legs and relatively small body also contributed to its remarkable running abilities, making it a formidable predator.
Another interesting adaptation of the Adasaurus was its reproductive method. Similar to modern birds, it was an egg-laying species. This method of reproduction allowed the species to lay several eggs at a time, increasing the chances of survival for their offspring.
The Adasaurus was believed to be diurnal, meaning it was active during the daytime. This activity pattern would have allowed it to bask in the warmth of the sun and hunt for food without the competition of other nocturnal predators. Its communication method is relatively unknown, as scientists have not yet discovered any evidence of vocalization or social behavior.
Being a top predator in its ecosystem, the Adasaurus played a vital role in maintaining the balance of the food chain. As a predator, it was responsible for controlling the population of its prey, which could have included small herbivorous dinosaurs and other small creatures in its environment. Its extinction would have had a profound impact on the ecosystem, potentially leading to the decline of other species.
The fossilized remains of the Adasaurus are primarily found in Mongolia, with some specimens also discovered in China. Its discovery in Mongolia is significant because it is the only known dromaeosaurid species found in this country. This fact has intrigued scientists, leading to further research and exploration in the area.
The fossil characteristics of the Adasaurus provide valuable insights into its anatomy and behavior. Partial skeletons have been unearthed, including a skull, ribs, vertebrae, and limb bones, allowing scientists to reconstruct its appearance and understand its locomotion. Additionally, traces of feathers have been found on some fossils, indicating that the Adasaurus may have been covered in feathers, much like its cousins, the Velociraptor and Deinonychus.
Despite its unique features and significant role in its ecosystem, the Adasaurus had a relatively short existence on Earth. Along with other non-avian dinosaurs, it became extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass extinction event about 66 million years ago. This event, believed to have been caused by an asteroid impact, wiped out nearly 75% of all species on Earth, including the Adasaurus.
In conclusion, the Adasaurus was a remarkable dinosaur, possessing unique features that set it apart from other theropods. Its lethal sickle claw, lightweight bone structure, agile running abilities, and specialized feeding habits make it a fascinating subject of study for paleontologists. Despite its extinction, its fossil remains continue to provide valuable information, giving us a glimpse into the prehistoric world of Mongolia.
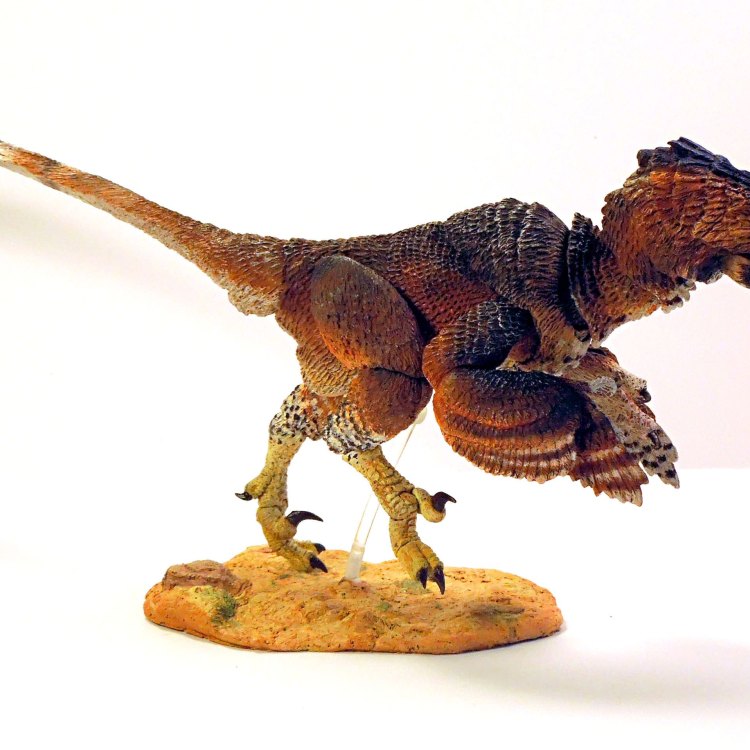

The Intriguing Story of Adasaurus: A Small but Fierce Late Cretaceous Dinosaur
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.